You are here
Geomodels
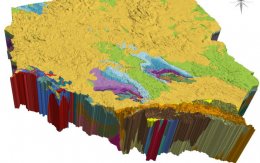
Geological Model of Poland
The country-wide Framework Geological Model of Poland, which serves as the foundation for modern geological cartography, was developed nearly two decades after creation of the first spatial model of Poland's geological structure within the range of -500 to -6000 m above sea level (Piotrowska et al., 2005), which was the world's first 3D geological model to span an entire country. Given the significant advancements in information technology and the growth of digital data resources over the past 20 years, there was a clear need to update and reconstruct the model to a more advanced version.
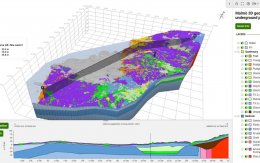
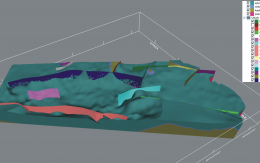
Malmö 3D geology for underground planning
Authors: Mikael Erlström, Jonas Ising, Linda Wickström, Björn Wiberg & Philip Curtis
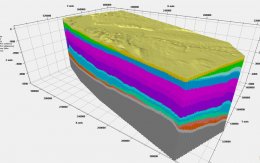
The geological 3D model of the Malmö–Lund area details the region's bedrock, soil types, geological development, and experience from infrastructure projects. The modeling was performed using the software Groundhog BGS © UKRI, developed by the British Geological Survey and the Natural Environment Research Council.
GeoTOP model of the Netherlands
The model GeoTOP provides a detailed three-dimensional view of the subsurface in the Netherlands until a maximum depth of 50 metres below NAP (Dutch Ordnance Level). GeoTOP schematises onshore Netherlands in millions of voxels (cells), each measuring 100 by 100 metres horizontally and 50 centimetres vertically. Each voxel in the model contains information on the lithostratigraphy and lithological classes, including the probability of occurrence for each lithological class. More info.
Groningen gas field
The Groningen gas field, located in the Netherlands, has ceased production on October 1, 2023, in accordance with the planned reduction in gas extraction that began in 2018 due to safety concerns and induced earthquakes.
GEUS 3D models
Geo3D web viewer can display models stored in external 3D model databases. In cooperation with geological survey of Denmark and Greenland GEUS we obtained rights to visualize models stored in EGDI 3D model database. In the link below we present a variety of 3D geological models created at GEUS.
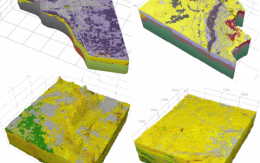
Parametric model
The parametric 3D geological model exemplifies a Jurassic layers in the western part of Poland, offering a generalized representation of lithologies and continuous properties related to porosity and rock density. These properties have been derived from the interpretation of data obtained through numerous seismic surveys and well drilling activities conducted in the region for oil and gas exploration, primarily within the underlying Upper Permian deposits.
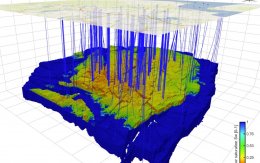
3D geological model of Gorzów block
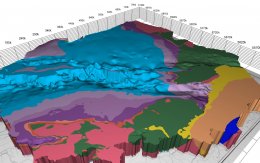
The geological model of Gorzów block shows the upper 5 000 m of the sedimentary stack of the block: from the roof of the Carboniferous up to the Quaternary. The model is based on most of the geological data collected so far in the area: 23 seismic volumes covering a total of 5500 square km, over a thousand 2D seismic lines, and wireline logs from 300 deep boreholes. Existing geological maps and gravimetric data were used in addition.
3DGP - model of Poland
The spatial model of geological structure of Poland presents the geological structure of Poland from depth of -6000 m above sea level to the surface. Three-dimensional solid models, geological cross-sections and blokdiagrams as well as spatial animations allow for analysis of deep geological structure. The model was implemented in two stages (from -6000 to -500 m above sea level and from -500 m above sea level to topo surface), using a variety of modeling tools.
Model of urban geology in Warsaw
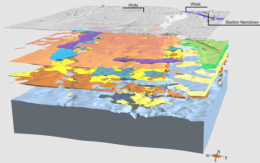
Project provides a detailed numerical model of the shallow geological structure of the urban agglomeration of the Warsaw area and its visualization within internet browsers. It presents the visualization of the common elements of the geological structure, i.e. the Żoliborz-Szczęśliwice valley, the deposits of Miocene brown coal.
Sedimentary cover of Lublin Basin
3D geological model of the Lublin Basin is the first step of the continuous programme of of 3D modelling of Poland's main sedimentary basins run by Polish Geological Survey (PSG). It is a methodical challenge in the light of the achievements in this field both in Poland and other countries, especially due to the huge data resource used in the model.